- The AEC is mainly an economic liberalization programme, aimed at increasing the international competitiveness of ASEAN and to make the ASEAN region as an attractive investment location.
- The AEC was formulated based on a pragmatic approach, adopting an FTA Plus approach and incorporating elements of common market. This was done, noting very well that ASEAN will not be able to achieve the EU-type of economic integration.
- The AEC has contributed towards increasing ASEAN global competitiveness, and extra and intra-ASEAN trade and investments; creating employment opportunities; and contributing to some extent in reducing the development gaps among Member States. The AEC has also contributed towards raising the per capita income in the region.
Roadmap to Economic Integration of ASEAN
1977 – 1992 : Preferential Trading Arrangement
1993 : ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA)
: Sub – Regional Economic Growth Areas (IMTGT, BIMP EAGA, Sijori, AMBDC)
1995 : ASEAN Framework Agreement on Services (AFAS)
1998 : ASEAN Investment Area (AIA)
2004 – 2010 : ASEAN FTAs with Dialogue Partner (China, Japan, Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand)
2008 – 2015 : Integration through AEAN Economic Community
- A single Market and Production Base;
- A competitive Economic Region;
- A Region with Equitable Economic Development; and
- A Regional Fully Integrated into the Global World
Target of AEC single market
- Single Market
- Free flow of goods
- Free flow of Services
- Free Flow Investment
- Free flow of Capital
- Free Flow of Skilled Labor
- Food Agriculture and Forestry - Competitive Economic Region
- PR
- Competition Policy
- Consumer Protection
- Infrastructure Development
- Taxation
- E-Commerce - Cooperation in Others Sectors
- Transport, Energy, Minerals, ICT, Tourism, Healthcare, Customs, Standards & Conformance - Equitable Economic Development
- SME
- Narrowing Development Gap - Integration into the Global Economy
- External Economic Relations
- Global Supply Networks
Benefits of integration to ASEAN
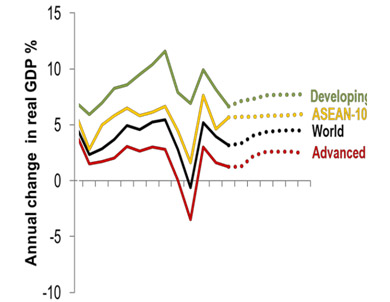
Source: International Monetary Fund’s (IMF) World Economic Outlook April 2013
- 4,435,670 Sq. Km.
- GDP Growth – 5-6 % per annum
- Increase in Per Capita - US$3,748 (US$1,917 in 2006)
- US$108.2 billion FDI Inflows
- Intra-ASEAN Investment – US$20 billion (18.5% of total ASEAN’s FDI)
- External Trade - US$2.47 trillion
- Intra-ASEAN Trade – US$601 billion (24 % of total ASEAN’s Trade)
- Reduction in Poverty Rate & Narrowing Development Gap